Document Type : Original Research Article
Author
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq
Abstract
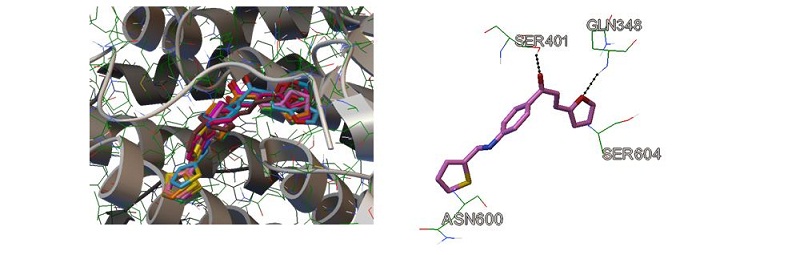
A new series of 3-furan-2-yl-1-p-aryl-propenone derivatives containing imine moieties (1-7) were synthesized and characterized using spectral analysis. The synthesized derivatives were screened in vitro against several bacterial species, including Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Gram-negative bacteria), and Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive bacteria) to study the effect of different imine moieties on the activity of (E)-1-(4-aminophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, which represent the potent hit against different bacterial species. The synthesized compounds were found to exhibit modest to vigorous activity, especially compounds 1, 4, and 6-7. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of compound 1 and 6 against Acinetobacter baumannii and Staphylococcus aureus were determined. The anti-biofilm activity of the potent discovered compounds (1, 4, 6, and 7) against Acinetobacter baumannii and Staphylococcus aureus were also determined. Docking study of the best discovered hits against the active site of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase, the antimicrobial target enzyme was achieved to explore the interactions of the synthesized hits inside the enzyme residues.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
Main Subjects